In the current global market, the diversity of languages presents one of the major challenges for businesses aiming to provide consistent customer service. Customers hail from various regions and communicate in many different languages, and neglecting this aspect can undermine trust, satisfaction, and brand image. Consequently, multilingual customer support is evolving into a necessity rather than merely a competitive edge. One of the most groundbreaking developments in this area is the incorporation of real-time translation technology into contemporary call centers. These systems facilitate live interaction between agents and customers speaking different languages without either party needing to be bilingual.
By utilizing real-time multi-language translation tools, call centers can guarantee that every customer is listened to, understood, and assisted—regardless of their native language. This fosters global inclusivity, enhances customer retention, and provides smooth, uninterrupted service delivery. With advancements in AI, machine learning, and speech technologies, businesses are now capable of creating more intelligent, agile, and language-neutral support systems than ever before. From small startups to large global corporations, adopting multilingual communication through technology is a strategic move toward achieving operational excellence and customer satisfaction.
What is a real-time multi-language translation call center?
A real-time multi-language translation call center is a support center enhanced by technology that allows agents to converse with customers in different languages instantly and naturally. These systems utilize AI-driven speech recognition, machine translation, and text-to-speech (TTS) or chat translation tools to establish a seamless linguistic connection. The agent can communicate in their chosen language, and the system automatically translates the message into the customer’s language, and the other way around. This facilitates smooth, bidirectional interaction, irrespective of the languages spoken by the participants.
In contrast to traditional call center,s where multilingual agents or interpreters are necessary, this system democratizes access to languages. It alleviates the challenge of recruiting language experts and enables any trained agent to cater to a global clientele. These systems accommodate numerous languages, are scalable according to demand, and often feature built-in error handling and real-time correction functionalities. Whether handling voice calls, live chats, support tickets, or emails, a multi-language call center can manage all communication channels with uniformity and clarity, thus providing a genuinely global-first customer experience.
How It Works
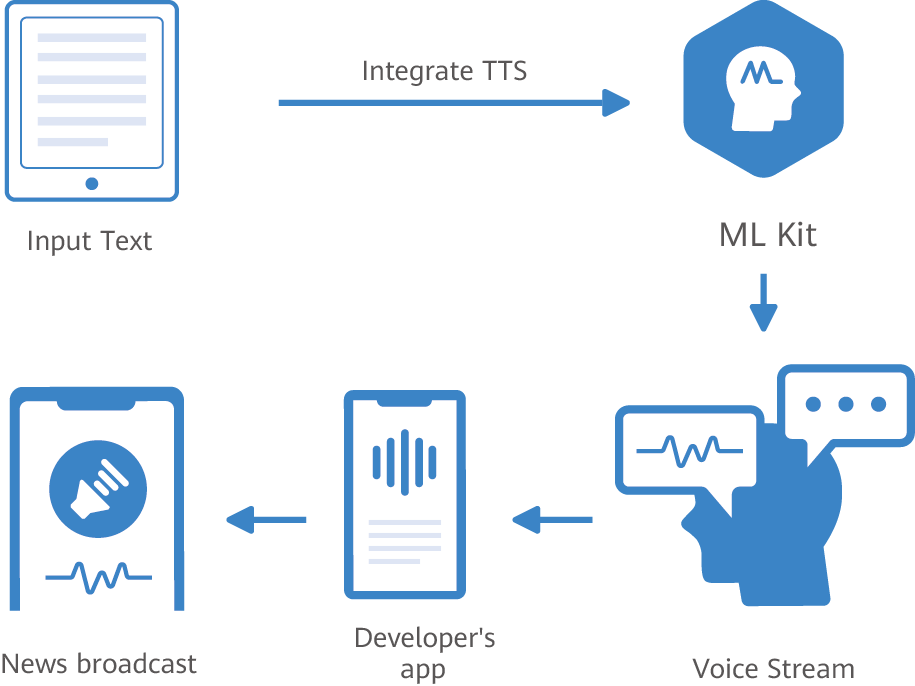
Real-time multi-language translation in modern call centers is facilitated by advanced technologies such as automatic speech recognition (ASR), machine translation (MT), text-to-speech (TTS), and natural language processing (NLP). When a customer starts a conversation in their language, ASR swiftly converts the spoken words into text. This text is subsequently processed through a machine translation system that promptly translates it into the agent’s preferred language. After the translated message is generated, the system either presents it as text or employs TTS to vocalize it to the agent, ensuring effective communication. The same sequence occurs in reverse when the agent replies. This two-way flow guarantees that both parties can comprehend and interact with one another in real time, regardless of their native languages.
Some sophisticated platforms even feature voice synthesis capabilities that imitate genuine tones and accents, rendering the interaction more personal and human-like. The whole procedure usually occurs within seconds, providing a user experience that is almost as seamless as a typical phone call. These tools are frequently incorporated directly into the call center software or customer relationship management (CRM) systems, facilitating easy access and use during real-time interactions. Furthermore, many solutions provide context-aware translation, which comprehends industry-specific jargon and modifies translations accordingly. This greatly enhances communication accuracy, particularly in technical support, healthcare, legal, or financial services. As AI progresses, the quality of translation is becoming increasingly natural and precise, minimizing misunderstandings and improving the customer experience.
Implementation Steps
Evaluate Language Needs: Before establishing a multilingual call center, it’s essential to comprehend your customer demographics. Reviewing customer data and support logs can uncover the most commonly spoken languages among your clientele. Once identified, prioritize these languages for translation assistance. This guarantees that your translation solution addresses the actual needs of your customers and aids in resource allocation effectively, focusing on the most influential languages for your business.
- Select a Translation Engine: The foundation of real-time translation depends on the engine that drives it. Choosing a dependable translation API is crucial for providing accurate and responsive communication. Leading providers like Google Cloud Translation, Microsoft Azure Translator, and Amazon Translate supply scalable APIs that can accommodate numerous languages in real time. Each service offers various features, including context-aware translation, personalized glossaries, and high-availability infrastructure. Select a solution that matches your technical environment and language requirements.
- Integrate with Call Center Software: To ensure a smooth customer journey, your translation solution should be integrated directly into your call center software or CRM platform. Services like ICTContact, Genesys, or Five9 frequently offer APIs or plug-ins that facilitate easy integration. This allows agents to access live translations, communicate with users seamlessly, and maintain comprehensive records of multilingual interactions. Effective integration also guarantees the scalability of your multilingual offerings across various support channels.
- Activate Speech Recognition and Text-to-Speech: To enable natural voice communication, implementing speech recognition and text-to-speech (TTS) technology is vital. Speech recognition transforms the customer’s spoken input into text for translation, whereas TTS converts the translated reply back into spoken words. This creates a real-time, voice-to-voice translation cycle. Contemporary systems also accommodate accent tuning and noise mitigation, enhancing both accuracy and user experience during live interactions.
- Educate Agents and Evaluate the System: Even with advanced technology, human training is crucial. Agents need to be instructed on how to utilize translation tools, interpret translated information effectively, and respond in ways that preserve customer trust. Conducting pilot programs and internal evaluations helps identify errors or delays in the system. These tests can be conducted in various scenarios and languages to assess response precision, latency, and user satisfaction prior to full implementation.
- Observe and Enhance: Following deployment, ongoing monitoring is vital for success. Regular reviews of analytics aid in assessing translation accuracy, conversation duration, and customer feedback. Pinpoint bottlenecks, latency challenges, or certain language discrepancies to refine your systems. Apply AI analytics to modify language models, enhance glossary application, and optimize real-time responses. Continuous updates and adjustments ensure your multilingual call center evolves alongside changing customer expectations.
Key Features
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
ASR technology captures oral communication and converts it into text with remarkable accuracy. In a call center context, this allows for immediate comprehension of customer inquiries in various languages. Contemporary ASR tools are capable of recognizing a variety of accents, dialects, and speech patterns, ensuring accessibility for users around the globe. The live transcription establishes the groundwork for subsequent translation, so its precision directly influences the quality of the interaction.
Real-Time Machine Translation (MT)
Machine Translation employs advanced AI and Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms to convert content between languages in real-time. Within a multilingual call center, MT effectively eliminates the communication barrier between the customer and agent nearly instantaneously. These systems continuously learn and adapt, improving accuracy based on context, sentence structure, and industry-specific vocabulary. Real-time MT guarantees that conversations seem smooth and agile, eradicating lengthy pauses or delays.
Text-to-Speech (TTS):
TTS transforms translated text into verbal language using synthesized voices that closely resemble human tone and inflection. For voice-driven interactions, TTS enables agents or systems to respond in the customer’s native tongue, even if the agent does not speak it. Sophisticated TTS systems can be tailored with voice profiles and emotional inflection, providing a more human-like and engaging experience during customer service interactions.
Language Detection:
Automatically recognizing the customer’s spoken or written language is a vital aspect of facilitating multilingual support. As soon as the customer starts communication, language detection tools evaluate the input to discern the language being used. Once recognized, the system seamlessly transitions to the correct translation setup, guaranteeing a smooth and prompt response without any manual configuration or lag.
Multilingual Chat and Voice Support:
To be effective, multilingual call centers need to accommodate both voice and text-based communication. Chat-based platforms incorporate translation engines to translate incoming messages and replies in real-time, while voice interactions utilize ASR, MT, and TTS for real-time conversations. Supporting both formats ensures comprehensive assistance across all support channels, whether customers choose to call, email, or chat online.
CRM Integration:
An effective translation system is not merely standalone—it needs to integrate thoroughly with your CRM or helpdesk software. Such integration enables agents to view customer histories, preferences, and past interactions, ensuring consistency and personalized service. This is particularly crucial when addressing ongoing problems or VIP clients, as it guarantees that language differences do not disrupt a high-quality customer experience.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis leverages AI to identify the emotional tone of customer messages, such as frustration, satisfaction, or urgency. In a multilingual setting, this capability gains even more significance by interpreting sentiment across different languages and cultures. Sentiment insights can be utilized to guide agent tone, escalate issues, or provide personalized solutions. This not only boosts customer satisfaction but also equips agents with emotional insights for enhanced engagement.
Challenges
- Accuracy and Context Sensitivity: Machine translation systems frequently encounter difficulties with context, idiomatic phrases, and industry-specific vocabulary, which can lead to possible misinterpretations. These challenges are particularly prevalent in intricate customer service situations or with technical terminology that may lack direct translations in other languages.
- Latency and Delay Issues: Real-time translation systems are required to process and deliver translations immediately to prevent interrupting the conversation flow. Even minor delays in translation can irritate customers and agents, impacting the overall experience. Achieving low latency presents a significant challenge in sustaining smooth communication.
- Accent and Dialect Recognition: Various accents and regional dialects can complicate speech recognition systems, resulting in misinterpretations or incorrect translations. These systems often find it challenging to process non-standard speech, making precise translations more difficult, particularly in multilingual or diverse environments.
- Security and Privacy Concerns: Processing sensitive customer information through third-party translation services raises considerable security and compliance challenges. There is a risk of revealing personal or confidential data, which can breach privacy regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. Ensuring that translation services adhere to data protection legislation is essential.
- Cost and Resource Management: Developing and sustaining a multilingual call center can be costly because of the technology and resources required. Companies must invest in translation software, integration with current systems, and specialized training for personnel, all contributing to a substantial expenditure.
Use Cases
- Global E-commerce Support: Real-time translation services empower e-commerce companies to assist customers worldwide, aiding in order placements, shipment tracking, and issue resolution. Multilingual support allows customers from various regions to easily navigate the platform and receive timely assistance, improving their overall experience.
- Travel and Hospitality: Travel agencies can provide multilingual support to accommodate tourists and travelers from various nations. Real-time translation guarantees that customers can book services, access travel information, and obtain emergency help in their native languages, enhancing satisfaction and trust in the service.
- Healthcare Services: In the healthcare sector, real-time translation assists in overcoming language barriers between patients and healthcare professionals. It enables patients to accurately articulate symptoms and convey their medical history, ensuring they receive appropriate care without miscommunication stemming from language differences.
- Banking and Financial Services: Real-time translation in banking guarantees that customers from varying linguistic backgrounds receive clear communication for financial operations, account management, and fraud mitigation. Providing multilingual support is vital for maintaining customer trust and security in the financial arena.
- Government and Emergency Services: Real-time translation allows governments and emergency services to provide critical assistance to citizens in their native languages. Whether it involves offering legal support, public health information, or responding to emergencies, these services ensure that language does not obstruct access to essential services.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Wider Customer Reach: Real-time translation facilitates access to global markets, enabling businesses to cater to a larger customer base and broaden their footprint across various regions. This is particularly significant for companies aiming to scale internationally.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Providing customer support in the customer’s native language creates an environment of trust and reassurance, resulting in increased levels of satisfaction. Customers feel more appreciated and are more inclined to remain loyal to companies that accommodate their language needs.
- Operational Efficiency: Instant translation minimizes the need to recruit multilingual agents or depend on human translators for each language. This results in enhanced operational efficiency, as companies can handle a wide variety of customer inquiries with fewer resources.
Cons:
- Translation Inaccuracies: In spite of progress in AI and machine translation, the technology continues to encounter difficulties in accurately translating intricate, context-sensitive content. Mistakes in translation can lead to misunderstandings or erroneous responses, which can negatively impact customer relationships.
- High Implementation Costs: The expenses associated with establishing and maintaining a real-time translation system can be considerable. Companies must invest in translation software, staff training, and ensuring system integration, which may impose a financial strain, particularly on small and medium-sized businesses.
- Technology Dependence: Call centers that depend on real-time translation systems are susceptible to potential outages, bugs, or errors within the translation engine. Such interruptions can influence communication quality and customer service, underscoring the necessity for dependable backup systems and redundancy measures.
FAQ’s
What is real-time translation in call centers?
Real-time translation refers to systems that immediately translate spoken or written communication during customer interactions, facilitating smooth conversations in various languages without delays or misunderstandings.
Which technologies are used for real-time translation?
Real-time translation systems utilize technologies like speech recognition, machine translation engines, and text-to-speech synthesis to translate languages in both directions, ensuring seamless communication.
Why should businesses use multilingual call centers?
Businesses can tap into a global customer base, enhance customer satisfaction by communicating in their native languages, and provide inclusive service that satisfies the diverse needs of customers worldwide.
How accurate is real-time translation?
While typically reliable, the accuracy of real-time translation can fluctuate depending on language complexity, context, and system quality. It is most effective with commonly used languages and straightforward, clear interactions.
How can real-time translation handle all languages?
Most systems support major languages, but they may offer limited assistance for regional dialects or lesser-known languages. Coverage may differ based on the capabilities of the translation system.