Introduction:
Linux servers are the spine of numerous organizations, fueling basic applications and administrations. To guarantee ideal execution, unwavering quality, and security, compelling organization, checking, and support are fundamental. In this comprehensive direct, we are going dig into the key angles of Linux server management, giving rules for victory within the ranges of Linux administration, server management, server observing, and server support.
Linux Administration:
Linux administration alludes to the management and upkeep of Linux-based operating systems. As Linux could be a well known choice for servers, viable organization is significant for guaranteeing the smooth operation and security of these frameworks. Linux chairmen are mindful for errands such as client administration, bundle establishment and upgrades, record framework management, and in general framework arrangement.
User management includes making and overseeing client accounts, setting up fitting authorizations and get to control, and guaranteeing secure verification. This guarantees that as it were authorized people can get to the framework and its assets.
Package management is basic for introducing, upgrading, and removing program bundles on a Linux framework. Bundle supervisors, such as well-suited, yum, and dnf, rearrange the method by dealing with conditions and giving a centralized store for program dispersion.
File system management includes working with the record frameworks utilized by Linux, such as ext4, XFS, or Btrfs. Directors handle assignments such as dividing disks, making and mounting record frameworks, and overseeing disk space. Normal support errands, like observing disk utilization and optimizing record frameworks, offer assistance keep up framework execution and avoid information misfortune.
Linux administrators are moreover dependable for server arrangement and setup. This incorporates selecting the fitting Linux dispersion, setting up the introductory server setup, and introducing required program bundles. Also, directors oversee administrations running on the server, guaranteeing their accessibility, performance, and security. This may include beginning, halting, and checking administrations like Apache, Nginx, MySQL, or other applications.
Security may be a significant viewpoint of Linux organization. Chairmen execute different security measures to ensure the server from unauthorized get to and assaults. This incorporates designing firewalls, executing interruption discovery frameworks, checking framework logs for suspicious exercises, and applying security patches and upgrades.
Linux administration plays a imperative part in keeping up the in general wellbeing and execution of Linux-based servers. By viably overseeing client accounts, bundles, record frameworks, server arrangement, and security, chairmen contribute to the steadiness, security, and productivity of the framework.Regular monitoring, maintenance, and proactive measures are key to successful Linux administration.
Linux Server Management:
Linux server management encompasses the activities involved in overseeing and maintaining the functionality, performance, and security of Linux-based servers. It involves various tasks, including server deployment, configuration, service management, security hardening, monitoring, and maintenance.
Server deployment and setup involve selecting the fitting Linux distribution and introducing it on the server hardware. Administrators set up the introductory server setup, design arrange settings, and guarantee that the server is legitimately coordinates into the existing foundation.
Service management includes supervising the administrations running on the server. This incorporates web servers (e.g., Apache, Nginx), database servers (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL), e-mail servers (e.g., Postfix, Sendmail), and other applications essential to back organizational needs. Chairmen are capable for beginning, halting, and checking these administrations to guarantee their accessibility and ideal execution.
Security hardening may be a basic viewpoint of Linux server management. Directors actualize security measures to ensure the server from unauthorized get to and assaults. This incorporates arranging firewalls, actualizing get to controls, empowering secure communication conventions (e.g., SSH), and applying security patches and overhauls frequently. Standard security reviews and powerlessness appraisals are performed to recognize and moderate potential dangers.
Monitoring the server is basic for distinguishing execution issues, asset utilization, and potential bottlenecks. Chairmen utilize different checking devices to track server measurements such as CPU utilization, memory utilization, disk utilization, and organize activity. This data makes a difference in recognizing execution debasement and taking proactive measures to optimize server execution.
Regular server support assignments incorporate overseeing reinforcements and fiasco recuperation plans. Administrators plan and actualize reinforcement methodologies to guarantee the accessibility and astuteness of basic information. This includes planning normal reinforcements, confirming the astuteness of reinforcements, and testing the reclamation prepare to ensure information can be recuperated in case of information misfortune or framework disappointment.
Additionally, administrators perform schedule upkeep exercises such as disk cleanup, log record turn, and framework upgrades. Frequently applying program overhauls and patches makes a difference address security vulnerabilities and guarantees the server remains up to date with the most recent highlights and bug fixes.
In general, Linux server administration requires a comprehensive approach to guarantee the server’s solidness, security, and ideal execution.By effectively deploying, configuring, managing services, implementing security measures, monitoring performance, and performing regular maintenance, administrators can ensure the smooth operation of Linux servers, supporting the organization’s needs efficiently.
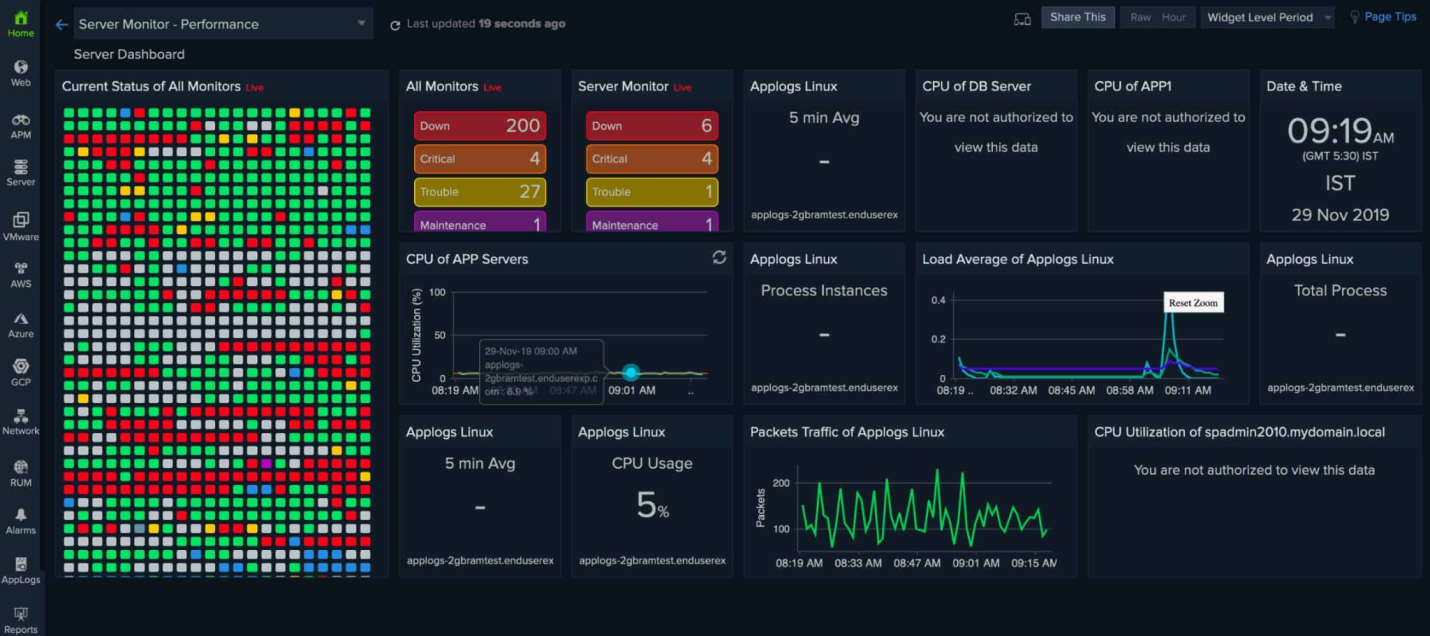
Linux Server Monitoring:
Linux server monitoring involves the systematic observation and measurement of key metrics and activities on a Linux-based server to ensure its optimal performance, availability, and security. Monitoring helps administrators identify and address issues promptly, prevent downtime, and optimize resource utilization.
System monitoring tools are utilized to gather information on different server measurements, counting CPU utilization, memory utilization, disk I/O, organize activity, and server uptime. These devices give real-time bits of knowledge into the server’s wellbeing and execution, permitting chairmen to identify peculiarities and take proactive measures.
Log monitoring and analysis play a significant part in Linux server checking. Framework logs contain profitable data approximately server occasions, blunders, and notices. Directors utilize log observing instruments to total and analyze logs, recognize issues or designs, and proactively address potential issues. This makes a difference in investigating issues, identifying security breaches, and keeping up framework judgment.
Performance monitoring and tuning are fundamental for optimizing server execution. Directors screen execution measurements like CPU stack, memory utilization, and reaction times to distinguish execution bottlenecks. By analyzing these measurements, chairmen can fine-tune framework settings, alter asset allotments, and optimize setups to make strides generally server execution.
Security monitoring may be a basic perspective of Linux server management. Administrators execute security checking instruments to distinguish and react to potential security breaches, unauthorized get to endeavors, or anomalous exercises. Interruption location frameworks (IDS) and security data and occasion administration (SIEM) apparatuses offer assistance in checking organize activity, distinguishing suspicious behavior, and creating cautions for quick activity.
Alerting and notification systems are indispensably components of server checking. Administrators set up cautions to get notices when predefined limits are surpassed or when particular events occur. This guarantees that directors are expeditiously educated of any basic issues, permitting them to reply in a convenient way and minimize downtime.
In addition to real-time observing, chronicled information examination is significant for capacity arranging and drift investigation. By analyzing authentic information, chairmen can recognize designs, figure future asset necessities, and make educated choices with respect to equipment overhauls, scaling, or optimization.
Overall, Linux server monitoring is crucial for keeping up the execution, accessibility, and security of Linux-based servers. By leveraging checking apparatuses, log investigation, execution optimization strategies, and security checking hones, chairmen can proactively distinguish and address issues, guarantee framework solidness, and provide a dependable and productive server framework.
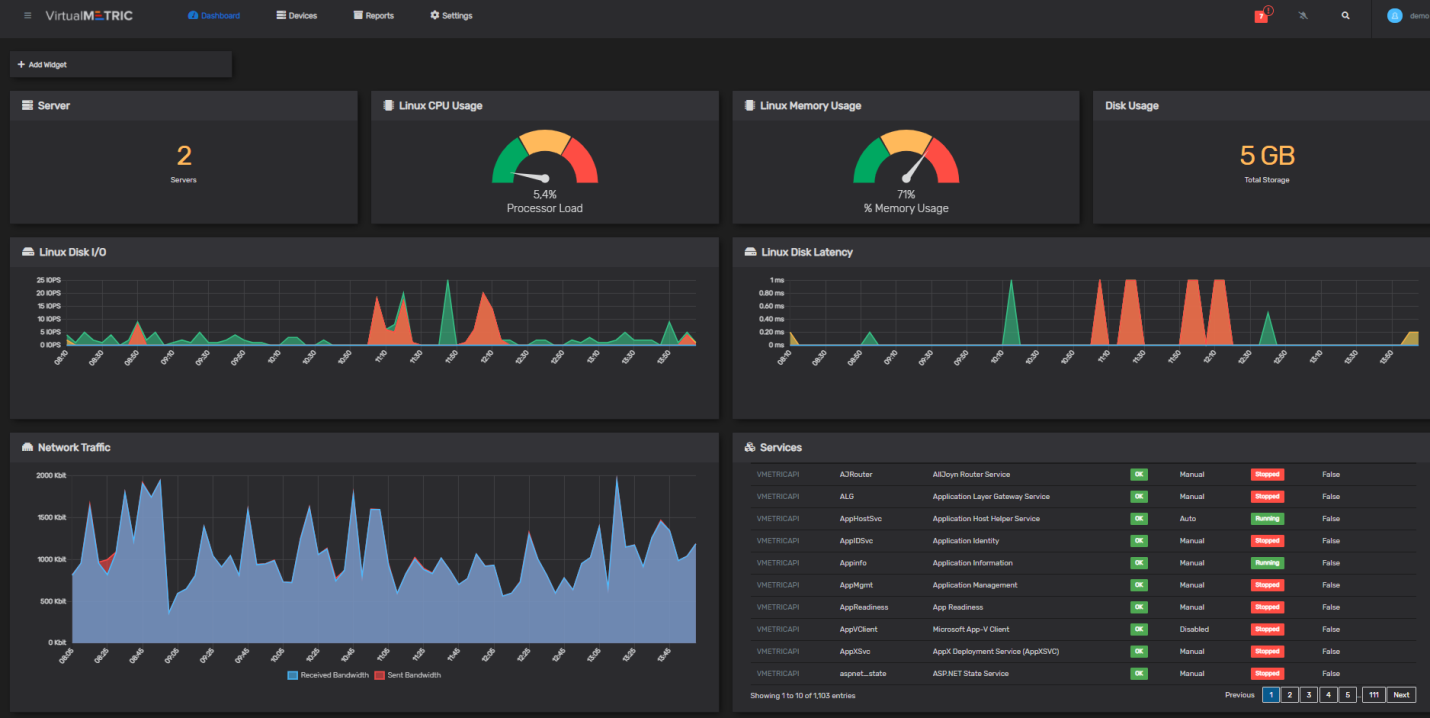
Linux Server Maintenance:
Linux server maintenance includes the continuous exercises required to keep Linux-based servers operating easily and proficiently. It incorporates different errands pointed at optimizing execution, guaranteeing unwavering quality, and tending to potential issues that will emerge amid the server’s lifecycle.
Regular maintenance tasks for Linux servers include:
Disk Space Management: Monitoring and managing disk usage is essential to prevent storage capacity issues. Administrators regularly check disk space utilization, remove unnecessary files, and perform disk cleanup to free up space and maintain optimal performance.
Log File Management: Log files provide valuable insights into system activities and potential issues. Administrators review and manage log files regularly, ensuring they don’t consume excessive disk space. They may set up log rotation mechanisms to archive or delete old log files automatically.
Hardware Monitoring: Monitoring hardware health is crucial to detect any potential hardware failures or malfunctions. Administrators utilize tools to monitor server components such as CPU, memory, disk drives, and network interfaces. Proactive monitoring helps identify and resolve hardware-related issues before they impact server performance or availability.
Performance Optimization: Administrators optimize server performance by fine-tuning various system parameters. This includes adjusting kernel settings, optimizing network configurations, and optimizing resource allocation to ensure efficient utilization of server resources.
Security Updates: Keeping the server up to date with security patches and updates is vital for maintaining a secure environment. Administrators regularly apply updates to the operating system, applications, and security software to address vulnerabilities and protect against emerging threats.
Backup and Disaster Recovery: Establishing a reliable backup strategy is essential to safeguard data and ensure business continuity. Administrators create backup schedules, perform regular backups, and validate the integrity of backups. They also design and test disaster recovery plans to ensure data can be restored in the event of a system failure or data loss.
System Upgrades and Migrations: Over time, system upgrades and migrations may be necessary to take advantage of new features, enhance performance, or address compatibility issues. Administrators plan and execute system upgrades and migrations carefully, ensuring minimal disruption to services and data integrity.
Documentation: Maintaining accurate and up-to-date documentation is essential for effective server maintenance. Administrators document system configurations, procedures, and changes made to the server environment. This documentation serves as a reference for troubleshooting, future maintenance, and knowledge transfer.
By performing regular server maintenance tasks, administrators can ensure the server’s stability, reliability, and optimal performance. It helps mitigate potential issues, enhances security, and minimizes downtime. Effective maintenance practices contribute to a robust and resilient Linux server environment.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Linux server management and maintenance are essential for ensuring the smooth operation, security, and performance of Linux-based servers. By effectively administering the server, managing services, implementing security measures, monitoring performance, and performing regular maintenance tasks, administrators can optimize the server’s functionality and minimize potential issues.
Linux administration includes errands such as client administration, bundle establishment, and record framework administration. Legitimate organization guarantees secure get to, program keenness, and proficient capacity utilization.
Server management includes sending, designing, and overseeing administrations running on the server. By guaranteeing benefit accessibility, execution, and security, directors contribute to a steady and responsive server environment.
Security could be a basic viewpoint of Linux server administration. Actualizing strong security measures, such as firewalls, get to controls, and customary upgrades, makes a difference ensure the server from unauthorized get to and vulnerabilities.
Checking the server’s execution, asset utilization, and potential bottlenecks is imperative for recognizing issues and optimizing execution. Normal support assignments like disk space administration, log record administration, and equipment checking contribute to a steady and solid server environment.
Standard reinforcements and catastrophe recuperation arranging are significant for information security and commerce coherence. By making successful reinforcement techniques and testing rebuilding forms, chairmen guarantee the accessibility and astuteness of basic information.
Linux server maintenance requires a comprehensive and proactive approach to keep the server working at its best. By executing these administration and upkeep rules, directors can accomplish victory in overseeing Linux servers, supporting organizational needs, and keeping up a secure and productive server environment.
Leveraging Open Source in ICT